Before We Begin…
This post is an overview of how we perform a ferrioxalate actinometer protocol to determine photon flux in our various photoreactors. We try to go into as much detail as possible so you can replicate these steps in your own lab and with your own equipment. Please check out some of our earlier posts if you’re interested in the foundations of actinometry or want some general background on how to measure light in photochemical reactions. And if this post helps you successfully measure your own photochemical reactions or equipment, we would love to hear about it! Reach out to us using the contact form or message us on Twitter @EvoluChem.
A Quick Description of The Ferrioxalate Protocol
This ferrioxalate actinometer protocol consists of irradiating a solution of ferrioxalate (Fe3+) to measure the production rate of Fe2+. The solution of ferrioxalate is made indiluted H2SO4. The resulting solution is light sensitive, so care should be taken to keep the room as dark as possible while running the protocol.
Samples are taken at specific points in timeand mixed with a AcONa (sodium acetate) buffer solution and phenanthroline solution to generate a phenanthroline Fe2+ complex.
The subsequent Fe2+concentration is then determined usingspectrometry measurement of the phenanthroline Fe2+ complex absorption at 510 nm. A calibration curve is madeusing FeSO4 solution and phenanthroline.
Synthesis of Ferrioxalate K3Fe(C2O4)3.3H2O
In the dark (under a red light) and at room temperature, combine 50 mL of a 1.5 M aqueous solution of FeCl3 (12.16 g) with 150 mL of a 1.5 M aqueous solution of K2C2O4.H2O (41.45 g). After 30 minutes, filter the solid off and recrystallize it 3 times in 50 ml of water. Store in an amber vial and place the solution in a desiccator overnight. Typically, 7-10 g are obtained. The resulting solid can be stored for months.
Reagents:
Actinometric Solution
This solution must be made in the dark as once the complex is in solution it reacts to all light. The solution is made from 9.03 g of K3Fe(C2O4)3, 12.2 mL 1N H2SO4 and 110 mL H2O. It should be stored at room temperature in a dark bottle wrapped in aluminum foil.
AcONa Buffer Solution
Mix 12 mL of AcONa solution (8.2g/100 mL), 7.2 mL 1N H2SO4 and 0.8 mL of H2O.
Spectrometric Solution
This solution is prepared for each sample by mixing 2.5 μL AcONa buffer, 100 μL of phenanthroline solution (0.1 g into 100 mL of H2O), and 892 μL H2O in a standard 96 deep well plate.
Actinometric Measurement
In a dark room under red light, prepare your setup with a light source and set your vial. NOTE: For a quick discussion of how best to evaluate light sources, please click here. Pipette the actinometric solution (in the tin foil bottle) into the vial. Irradiate the vials for exactly 5 or 10 second intervals taking 5 μL samples and transferring them to the clear 96 well plate containing the spectrometric solution. NOTE: You should be wearing protective orange goggles when the light is on. Once irradiation is over, transfer 200 μL of each sample to a reading 96 well plate. Wrap the plate in aluminum foil as it is still light sensitive. Measure the sample absorption with a plate reader at 510 nm.
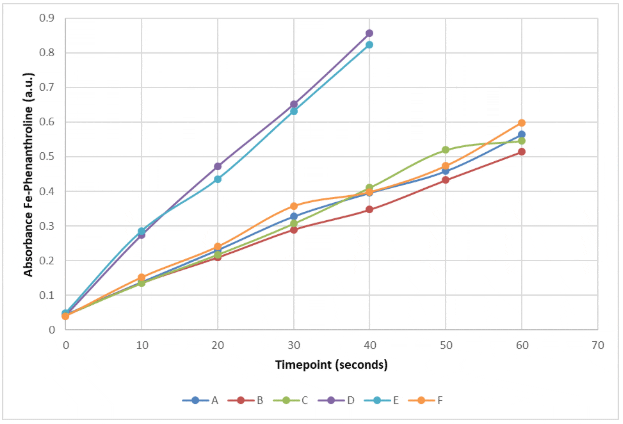
Example of Fe-Phenanthroline complexe absorbance measurement of experiment timepoints. Six different vials (A, B, C, D, E, and F) at different position from a light source.
Calibration Curve Preparation
Prepare a 0.4 mM ferrous solution, by adding 278.01 mg of FeSO4, 7 H2O (278.01 g/mol, 1 mmol) in 1 mL of H2SO4 (1 N) and dilute to 10 mL with H2O (0.1 M). Then transfer 80 μL into 2 ml of H2SO4 (1 N) diluted into 20 mL (4 mM).
Prepare buffer-phenanthroline solution, by adding 477.15 mg AcONa and 10.99 mg phenanthroline together, and then dissolve in 6 mL H2O. Add 3.6 mL 1N H2SO4 and 0.4 mL H2O.
Prepare the 9-point calibration in a 96 deep well plate by mixing the FeSO4 solution, buffer-phenanthroline solution and H2O with the volumes described below. Let the solution sit for 30 minutes. Transfer 200 μL in a flat bottom transparent well plate. Measure the sample’s absorption on a plate reader at 510 nm.
| Fe2+ Concentration (mM) | Volume buffer-phenanthroline solution | Volume 0.4mM FeSO4 | Volume H2O |
| 0 | 350 μL | 0 | 650 μL |
| 0.02 | 350 μL | 50 μL | 600 μL |
| 0.04 | 350 μL | 100 μL | 550 μL |
| 0.06 | 350 μL | 150 μL | 500 μL |
| 0.08 | 350 μL | 200 μL | 450 μL |
| 0.1 | 350 μL | 250 μL | 400 μL |
| 0.12 | 350 μL | 300 μL | 350 μL |
| 0.14 | 350 μL | 350 μL | 300 μL |
| 0.16 | 350 μL | 400 μL | 250 μL |
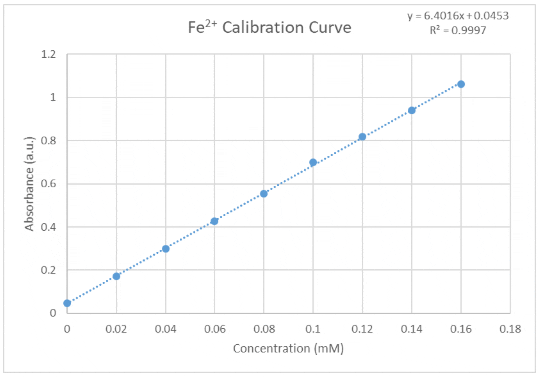
Typical calibration curve
Determine Photon Flux In Your Photochemical Experiments
To find out how to calculate the photon flux using your results, check out our post Determining Photon Flux Using Actinometry.
Did this post help you successfully measure your own photochemical reactions or equipment? We would love to hear about it! Reach out to us using the contact form or message us on Twitter @EvoluChem.

